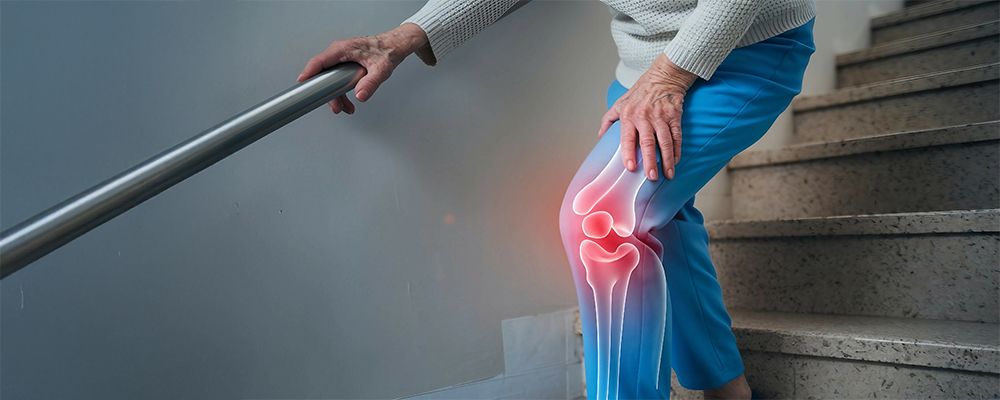
Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Knee osteoarthritis is a condition in which the protective cartilage that cushions your knee joint gradually wears away. Cartilage is essential for smooth, pain-free movement between bones. When it starts to break down, the bones in your knee begin to rub against each other, leading to pain, swelling, stiffness, and limited mobility.
This condition is classified as a degenerative joint disease and tends to worsen over time. The knee is especially vulnerable because it bears much of the body’s weight and absorbs impact during everyday movements. Although there is no cure for osteoarthritis, there are effective ways to manage the symptoms and slow its progression. Lifestyle changes, physical therapy, medications, and advanced non-surgical procedures can offer significant relief. In severe cases, joint replacement surgery may be recommended.
COMMON SYMPTOMS OF KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS
The most prominent symptom of knee osteoarthritis is pain that worsens with movement or prolonged inactivity. These symptoms may start out mildly and become more persistent or intense over time.
Morning stiffness or stiffness after sitting for long periods
Swelling or a sense of puffiness around the knee
A cracking, popping, or grinding sound when bending the joint
A feeling of instability, as if the knee might “give out”
Difficulty in fully bending or straightening the knee
Causes
The breakdown of cartilage in the knee occurs gradually and may be influenced by a range of factors. Common causes include:
- Aging: Natural wear and tear with age is the most common cause.
- Previous joint injury: Old sports injuries or trauma can contribute to early joint degeneration.
- Repetitive stress: Jobs or activities that involve frequent kneeling, squatting, or heavy lifting may speed up cartilage damage.
- Joint misalignment: Conditions like “knock knees” or bowlegs can place uneven pressure on parts of the joint.
- Genetics: A family history of osteoarthritis can increase your risk.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the joint can accelerate cartilage loss.
- Obesity: Excess body weight increases strain on the knee, hastening joint wear.
Risk factors
Several factors can make a person more likely to develop knee osteoarthritis. These include:
- Having a high body mass index (BMI), especially 30 or above
- Sustaining a previous knee injury
- Engaging in physically demanding work or sports
- Inheriting a genetic predisposition to joint issues
- Having abnormal joint structure or alignment
Being aware of these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures earlier in life.
Stages
Although not always clearly categorized, knee osteoarthritis tends to progress in stages:
- Stage 1 (Mild): Minor cartilage wear, typically without noticeable symptoms.
- Stage 2 (Early): Cartilage begins to thin. Pain and stiffness may occur during or after activity.
- Stage 3 (Moderate): Significant cartilage damage leads to more frequent pain, reduced range of motion, and occasional joint instability.
- Stage 4 (Severe): Most or all cartilage is lost. Bones rub together directly, causing constant pain, swelling, and joint immobility.
Diagnosis
To diagnose knee osteoarthritis, a healthcare provider will begin with a physical examination and a discussion about your symptoms. They will look for signs such as:
- Swelling, tenderness, or discoloration around the knee
- Pain during movement or when pressing on specific areas
- Limited range of motion or a sensation of joint looseness
- Abnormal gait or difficulty walking
TDiagnostic imaging, such as an X-ray, is typically used to assess the extent of joint damage. In some cases, an MRI or CT scan may be recommended to examine soft tissues more closely.
Minimally Invasive Treatment Options
Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE)
One of the innovative, minimally invasive treatment options for knee osteoarthritis is Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE). This image-guided procedure targets the inflamed lining of the knee joint without requiring open surgery.
GAE involves inserting a small catheter through a tiny puncture in the upper thigh. Using real-time X-ray imaging, the doctor navigates the catheter to the genicular arteries—small vessels supplying the inflamed joint tissue. Once positioned, tiny medical particles are released to reduce blood flow to the affected areas. This decrease in blood supply helps reduce inflammation, which in turn alleviates pain, swelling, and stiffness. It is performed under light sedation. The procedure typically takes under 90 minutes, and most patients return home the same day.
Genicular Nerve Radiofrequency Ablation
Genicular nerve radiofrequency ablation, also known as genicular radiofrequency ablation (RFA), is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat chronic knee pain caused by osteoarthritis when conservative treatments have failed. During this outpatient procedure, a physician uses radiofrequency energy to heat and disrupt the genicular nerves that carry pain signals from the arthritic knee joint to the brain. The treatment involves inserting thin needles guided by fluoroscopic imaging to precisely target the genicular nerves around the knee, then applying controlled heat to create small lesions that interrupt pain transmission. This procedure can provide significant pain relief lasting 6-12 months or longer, allowing patients to reduce pain medication use, improve mobility, and delay or avoid knee replacement surgery. Genicular nerve ablation is particularly beneficial for patients who are not candidates for surgery or prefer a less invasive approach to managing their osteoarthritis pain.
What Are My Other Treatment Options?
Conventional options include:
- Physical therapy
- Over-the-counter or prescription pain medications
- Joint injections
- Knee replacement surgery (for advanced cases)
GAE is ideal for those who haven’t responded to these treatments or are not ready or fit for surgery. It also serves as a bridge to surgery when needed.
Why Choose GAE Over Other Traditional Treatments?
- Minimally Invasive: No incisions or bone removal
- Outpatient-Based: No hospital stay
- Quick Recovery: Back to daily life in 1–2 days
- Effective Pain Relief: Relief typically begins in 2 weeks
- Preserves Future Options: Doesn’t rule out knee replacement
- Less Medication: Reduces dependence on painkillers and steroid injections
How Does GAE Work at RIVEA?
Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE) is a non-surgical, image-guided procedure performed by our expert interventional radiologist. It targets the small arteries supplying blood to the inflamed synovium (joint lining) in the knee. Here's what to expect:
- Performed under twilight sedation – no general anesthesia.
- A tiny puncture is made in the groin or thigh to access an artery.
- A catheter is guided to the genicular arteries using live X-ray.
- Medical-grade microspheres are released to block abnormal blood flow.
- Inflammation is reduced, relieving pain and improving knee function.
- Most patients go home the same day, with minimal downtime and no stitches.
Learn more about Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE)
Why Choose RIVEA?
At RIVEA Vascular Institute in Hyderabad, we combine technology, expertise, and compassion to offer world-class interventional care. Our team specializes in advanced image-guided procedures designed to reduce pain and improve your quality of life without major surgery. Every patient receives a tailored plan with direct access to their treating specialist, minimal wait times, and comprehensive support throughout their care journey.
Click here to learn more about:
Genicular Artery Embolization (GAE)
For any inquiries, post your query here:
Ask Rivea
Contact us today to explore your options.
Call Now
Our Team
-

Dr. Arjun Reddy
MBBS, MD
Chief Interventional RadiologistDr. Arjun Reddy is a highly accomplished Interventional Radiologist with extensive international training and a track record of pioneering minimally invasive, image-guided procedures in India.
View Profile Book an Appointment