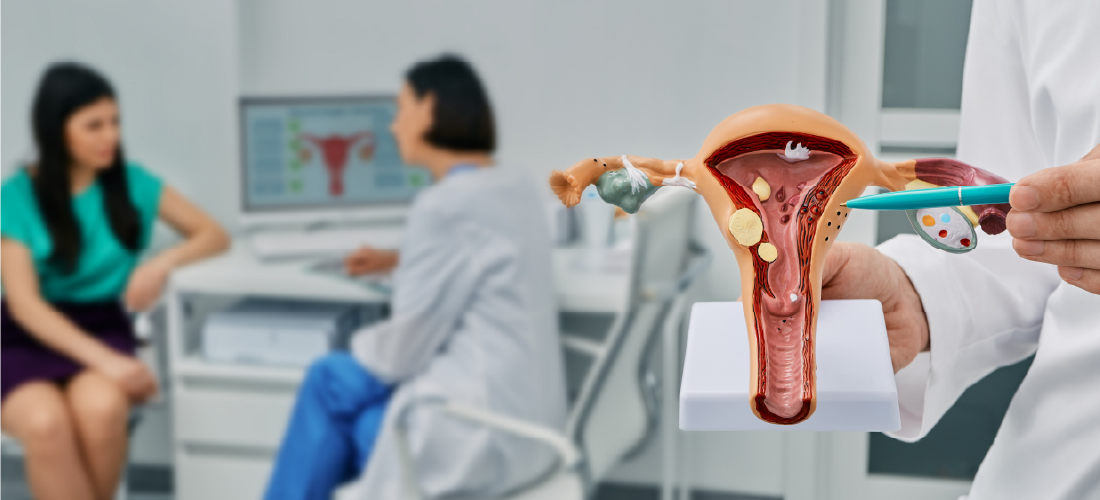
Uterine Fibroid Embolization
Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths that develop in or around the uterus. They affect a significant percentage of women, particularly during their reproductive years. Fibroids are usually benign, though they can lead to substantial symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, frequent urination, bloating, and even infertility. For women seeking relief from these symptoms without undergoing major surgery, RIVEA, Hyderabad offers Uterine Fibroid Embolization treatment: a safe, effective, and minimally invasive option for non-surgical fibroid removal.
Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) is a well-established procedure performed by interventional radiologists . They use advanced imaging techniques to block the blood supply to fibroids, causing them to shrink over time. With an excellent success rate and quicker recovery compared to traditional surgical interventions, Uterine Fibroid Embolization is increasingly being recognized as a first-line treatment for symptomatic fibroids.
When is Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) performed?
UFE is most commonly used to treat symptomatic uterine fibroids, which can manifest in a variety of ways, including:
- Heavy, prolonged menstrual bleeding (sometimes with clots)
- Pelvic pressure, pain, or fullness
- Frequent or urgent urination due to bladder compression
- Constipation or bloating due to pressure on the bowel
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Infertility caused by fibroid-induced distortion of the uterine lining
- Anemia resulting from excessive blood loss
- Lower back or leg pain due to fibroid pressure on nerves
- Abdominal enlargement mimicking pregnancy
Understanding Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
Who Should Consider Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)?
UFE is increasingly recognised as a preferred option for women who want effective relief without the physical and lifestyle disruption of major surgery. It offers meaningful symptom improvement while allowing women to maintain normal routines, fertility potential, and overall uterine health.
UFE is particularly beneficial for:
- Women whose symptoms persist despite medication - Ideal for those still experiencing heavy bleeding, pelvic pain, or pressure.
- Patients seeking a uterus-sparing, fertility-preserving alternative to surgery (hysterectomy/myomectomy) - UFE treats fibroids without removing the uterus or altering anatomy.
- Women who are not ideal candidates for surgery - Especially helpful for individuals with medical conditions that increase surgical or anaesthesia risk.
- Individuals with multiple or surgically difficult-to-access fibroids - UFE treats fibroids across the uterus, regardless of size, number, or location.
- Working women who need a quicker return to routine - With its short recovery time, UFE allows most women to resume regular activities within days.
Choosing the right fibroid treatment should always follow a comprehensive clinical assessment, including imaging and symptom review. Early detection of fibroids widens the range of available options, often making minimally invasive treatments like UFE possible before symptoms progress or surgical intervention becomes necessary.
How to prepare for Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)
The patient will undergo a comprehensive evaluation, including MRI or ultrasound imaging, to assess the size and location of the fibroids.
- The healthcare provider will review medical history, medications, allergies, and discuss fertility goals.
- If necessary, a biopsy may be taken to rule out other conditions.
- The patient will be instructed to stop eating and drinking at least 6 hours before the procedure.
- A pregnancy test is usually administered, as X-ray exposure can be harmful to a fetus.
What Happens During the Procedure?
Uterine Fibroid Embolization is a proven non-surgical treatment for uterine fibroids, helping women avoid the risks and long recovery associated with traditional surgery. UFE is typically performed on an outpatient basis, meaning most patients can return home the same day. However, some may choose to stay overnight depending on their condition or pain tolerance.
- The patient will lie on an examination table and receive sedative and intravenous (IV) antibiotics to prevent infection.
- Local anesthesia will be administered to numb the area—either near the groin (femoral artery) or wrist (radial artery), depending on what the doctor recommends.
- A tiny incision is made, and a catheter is inserted into the artery. Fluoroscopy (live X-ray imaging) and contrast dye are used to guide the catheter to the uterine arteries.
- Once in position, tiny particles (about the size of sand grains and made of medical-grade plastic or gelatin) are injected through the catheter.
- These particles block blood flow to the fibroids, depriving them of oxygen and nutrients.
- The catheter is then removed, and pressure is applied to stop any bleeding at the puncture site.
The procedure typically takes 60 to 90 minutes. Because the fibroids are no longer receiving blood, they begin to shrink and die off over the following weeks to months.
What happens after Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)?
The UFE procedure typically lasts 1 to 1.5 hours, with additional time needed for preparation and post-procedure monitoring.
Most people can leave the hospital within a few hours after a uterine fibroid embolization. Some other things to expect afterward include:
- Pain medication and antibiotics may be prescribed for home use.
- Watery or mucus-like vaginal discharge can persist for several weeks.
- Pelvic pain, cramps, and discomfort may continue for up to two weeks.
Most people are able to return to regular activities within 7–10 days, though fatigue may last longer. Up to 90% of patients resume normal routines within 10 days of the procedure. Patients treated through the groin may need longer hospital recovery to monitor the puncture site, while those treated through the wrist can often walk and recover more quickly.
It’s common to temporarily miss menstrual cycles. When periods resume, they may be lighter at first, gradually increasing but usually remaining improved compared to pre-procedure levels. For fibroid treatment, symptom relief typically begins within 2–3 weeks.
In some cases, fibroid tissue may be passed vaginally. Most fibroids shrink over time and stop causing symptoms, even if they remain attached to the uterine wall. Significant symptom improvement is usually noticeable within three months, with full relief often seen by six months post-procedure.
Aftercare
- Keep the groin incision clean and dry once you are home. Follow your provider’s instructions for bathing.
- If adhesive strips were applied, keep them dry. They will typically fall off on their own in a few days.
- Use only the pain medications recommended by your provider. Avoid aspirin or similar medications unless approved, as they can increase bleeding risk.
- Light walking is usually encouraged, but avoid strenuous activities until your provider gives the all-clear.
- Stay hydrated and eat a fiber-rich diet to help prevent constipation. Straining during bowel movements can interfere with healing. A mild laxative may be recommended if needed.
Watch for any signs of complications and contact your provider if you experience:
- Fever or chills
- Redness, swelling, or unusual discharge from the incision site
- Increased pain near the incision
- Abdominal cramping, pain, or swelling
- Heavy vaginal bleeding or passage of tissue or unusual fluid
A follow-up appointment is usually scheduled 1 to 2 weeks after the procedure.
Your provider may order imaging tests such as an ultrasound or MRI about 6 months later to evaluate the outcome of the procedure.
Why Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) may be the best choice:
Minimally invasive with only a small skin puncture
Faster recovery than traditional surgery
Reduced bleeding risk and complications
Lower complication rate than hysterectomy or myomectomy
No hormonal side effects
90% experience symptom relief
Preserves uterus and fertility potential
Why choose RIVEA for UFE?
At RIVEA, we specialize in non-surgical, image-guided treatments for fibroids, prioritizing precision, safety, and patient comfort. You will be treated by a dedicated uterine fibroids specialist with expertise in advanced, minimally invasive procedures. Our uterine fibroid embolization (UFE) program is led by experts trained in advanced interventional radiology techniques. Our uterine fibroid embolization specialist, Dr. Arjun Reddy, is known for his expertise as one of the best UFE treatment doctors in Hyderabad. We are also trusted for providing fibroid removal without hysterectomy in India, helping women retain their uterus while relieving symptoms. If you are searching for safe and effective uterine fibroids treatment in Hyderabad, RIVEA offers one of the region’s most trusted centers for patient-focused care. Driven by the vision of becoming the top hospital for uterine fibroid embolization in Hyderabad, India, RIVEA integrates clinical expertise with state-of-the-art technology to provide safe, precise, and individualized patient care.
At RIVEA, you can expect:
- Allia IGS 7 hybrid imaging system for ultra-precise minimally invasive procedures
- Personalized consultation and care plans tailored to your needs
- Faster access to treatment with no prolonged waiting times
- Outpatient procedure convenience with high safety standards
Whether you are experiencing heavy bleeding, pelvic discomfort, or a sense of pressure, our team provides advanced care for uterine fibroids in Hyderabad, India, prioritizing your comfort, recovery, and long-term health. Schedule a consultation to learn more about uterine fibroid embolization and other minimally invasive treatment options.
FAQs
What is Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE)?
UFE is a minimally invasive, non-surgical procedure performed by interventional radiologists. It treats fibroids by blocking the arteries that supply them with blood, causing the fibroids to shrink while preserving the uterus.
Who is eligible for UFE?
Women with symptomatic fibroids—such as heavy periods, pelvic pain, bloating, frequent urination, or fertility concerns—are potential candidates for UFE. A consultation with an interventional radiologist helps determine suitability.
How is UFE different from hysterectomy or myomectomy?
Unlike hysterectomy, UFE does not involve removing the uterus. It’s less invasive than myomectomy and typically has a much faster recovery time, with fewer risks and no visible scars.
Does UFE hurt?
UFE is performed under local anesthesia and mild sedation. Some cramping or discomfort is common in the first few days post-procedure but is usually manageable with pain relief medications.
How long does the procedure take?
UFE usually takes between 45 minutes to 1.5 hours. Most patients can return home within 24 hours.
What is the recovery time after UFE?
Most women return to light daily activities within 7–10 days. Full recovery generally takes a few weeks, much quicker than after surgical procedures.
How effective is UFE?
Studies show that 85–90% of women experience significant symptom relief after UFE, including reduced bleeding, pain, and pressure.
When is Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE) not recommended?
While UFE is highly effective, it is NOT recommended for individuals who:
- Are currently pregnant
- Have fibroids but no symptoms
- Have a pelvic infection
- Have diseases affecting veins or arteries
- Are allergic to contrast dye used during the procedure
Will UFE affect my ability to get pregnant?
UFE preserves the uterus, unlike hysterectomy. However, the impact on fertility depends on individual cases. Women interested in future pregnancy should discuss risks and alternatives with their doctor.
Can fibroids come back after UFE?
Recurrence is possible but occurs in approximately 25–31% of cases over several years, similar to surgical treatments like myomectomy.
What are the potential risks of UFE?
UFE is considered a safe and effective procedure, but like all medical interventions, it carries some risks. Understanding these risks is crucial in making an informed decision. Potential complications may include:
- Infection in or around the uterus or fibroids
- Injury to the uterus or surrounding tissues due to unintended embolization
- Allergic reactions to contrast dye or medications
- Hematoma (collection of blood) at the catheter insertion site
- Permanent or temporary loss of menstrual periods (amenorrhea), particularly in women over 45
- Infertility, especially if complications arise or if blood flow to the ovaries is affected
- In rare instances (1–2% of cases), a hysterectomy may be required if complications occur or symptoms persist.
Is UFE safe?
Yes. UFE is recognized by leading global health organizations as a safe and effective fibroid treatment. Major complications occur in less than 1% of cases when performed by trained specialists.
Click here to learn more about:
Uterine Fibroids
For any inquiries, post your query here:
Ask Rivea
Contact us today to explore your options.
Call Now
Our Team
-

Dr. Arjun Reddy
MBBS, MD
Chief Interventional RadiologistDr. Arjun Reddy is a highly accomplished Interventional Radiologist with extensive international training and a track record of pioneering minimally invasive, image-guided procedures in India.
View Profile Book an Appointment